What is Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome?
Even with care and proper training, it is still possible for some athletes to suffer a form of injury. One of the most common is called the runner’s knee or jumper’s knee, known to doctors as patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS).

Causes of PFPS
PFPS is the most common condition that causes pain around and under the kneecaps in most athletes, but anyone can also get it even those who have a sedentary lifestyle. However, even doctors still cannot pinpoint the exact cause PFPS although it is associated with several factors.
One is overuse of the legs, especially with repetitive stress. This leads to irritation. Second, is injury to the kneecap such as a fracture or a dislocation. Third, surgery on the knees after suffering from an injury can also lead to PFPS. This is especially common in cases where the anterior cruciate ligament is affected because the patellar tendon will be used by the surgeon as graft. Fourth is the muscle weakness or muscle imbalance. Conditions that affect the alignment of the hip and knee muscles increase the risk of getting PFPS.
Sports that require squatting, running, and jumping can especially be hard on the knees. Other factors such as age, gender, and the sport you participate in will also matter. Arthritis increases the risk of PFPS especially in the elderly, although PFPS affects mostly the young and active. Women are also more likely to have PFPS because of the wide pelvis and the subsequent angle alignment to the knee joints.
Symptoms of PFPS
The name patella refers to the area around the kneecap, which means that the pain will be more pronounced as the person walks, runs, walks up or down the stairs, squats, and sits for a prolonged period. The tell-tale sign of PFPS is the dull pain on the front knee.
Sometimes the knees pop or crack when performing any act, but if the person experiences a locking knee joint, this could indicate a different condition called meniscal tear, which is different from PFPS but share the same symptoms. PFPS does not cause excruciating pain that is why most people ignore it and associate it with old age. To diagnose PFPS, the doctor needs to conduct a physical exam through motion exercises. Only will imaging tests be required if some symptoms point to other types of injuries.
Treating PFPS
PFPS is not easy to treat because some patients successfully recover with rest, but there are others who will eventually suffer from permanent pain. In fact, there is no sure method or medication to treat PFPS, that is why it is important that you discuss this openly with your doctor especially if you are an athlete. PFPS is misunderstood even among experts starting with its name.
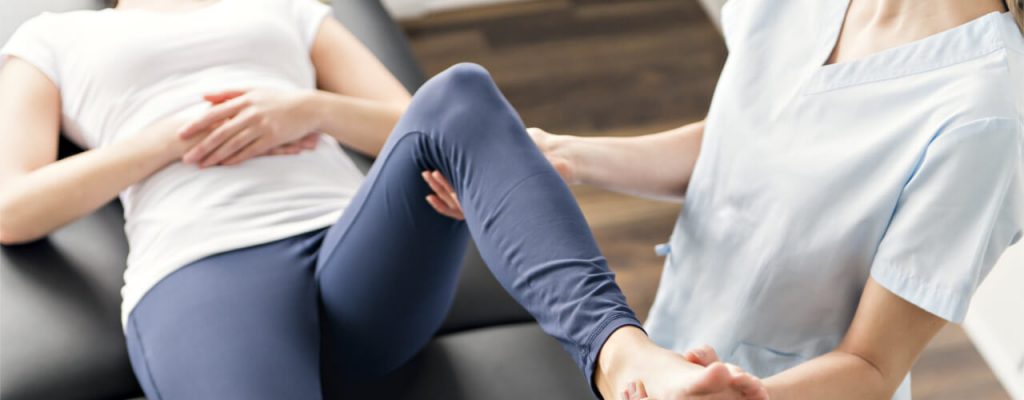

Conventionally, PFPS is treated through medications, therapy or surgery depending on the severity of the symptoms. Pain relievers may be needed but therapy such as supportive braces, rehabilitation, ice compress, and taping are required. If there is no improvement, surgery such as realignment of the kneecap or arthroscopy to remove damaged cartilage may be necessary.

Hi, Stranger! Leave Your Comment...